Debunking the Climate Scam
Billions of Dollars -
Greedy Green Corporations -
No Warming For Two decades -
Bought and Paid For Organizations

TWO PAPERS -
New study shows half of the global warming in the USA is artificial
Posted on July 29, 2012 by Anthony Watts
PRESS RELEASE – U.S. Temperature trends show a spurious doubling due to NOAA station siting problems and post measurement adjustments.
Chico, CA July 29th, 2012 – 12 PM PDT – FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
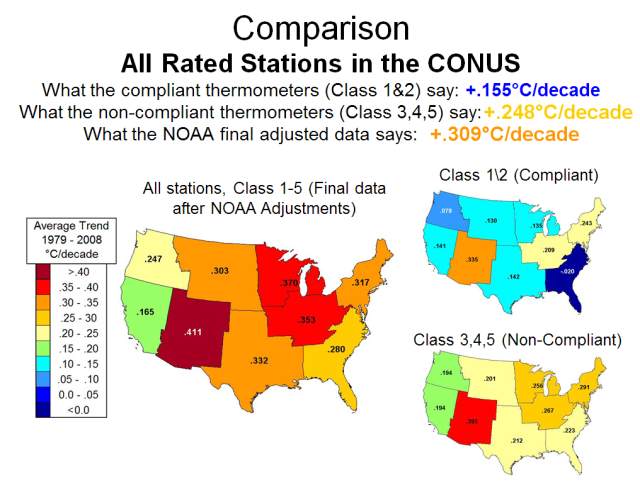
A comparison and summary of trends is shown from the paper. Acceptably placed thermometers away from common urban influences read much cooler nationwide:
A reanalysis of U.S. surface station temperatures has been performed using the recently
WMO-
The new improved assessment, for the years 1979 to 2008, yields a trend of +0.155C per decade from the high quality sites, a +0.248 C per decade trend for poorly sited locations, and a trend of +0.309 C per decade after NOAA adjusts the data. This issue of station siting quality is expected to be an issue with respect to the monitoring of land surface temperature throughout the Global Historical Climate Network and in the BEST network.
Today, a new paper has been released that is the culmination of knowledge gleaned from five years of work by Anthony Watts and the many volunteers and contributors to the SurfaceStations project started in 2007.
This pre-
Read the whole story at http://wattsupwiththat.com/2012/07/29/press-
Chineese Paper: up to 68% of warming is false
The Chinese demonstrate that UHI has a real and essential effect on regional climate change
Posted on May 13, 2013 by Anthony Watts
Study finds that urbanization has considerable influence on the regional climate
change, they even blame proximity to air-
Press release from Science China Press (full paper follows)
Urbanization and surface warming in eastern China
A recent study indicated that the urbanization in eastern China has significant impact
on the observed surface warming and the temporal-
This work was led by YANG XiuQun, professor of meteorology in the Institute for Climate and Global Change Research, School of Atmospheric Sciences at Nanjing University. The article entitled “Urbanization and heterogeneous surface warming in eastern China” was published in Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, No. 12.
Urbanization, as one of the most significant processes in land use/cover change, can not only alter surface vegetation distribution, but also affect surface energy and water balance. Some previous studies indicated that urbanization has little impact on surface warming. However, recent investigations have suggested that urbanization plays an essential role in regional climate change.
China has been experiencing intensive urbanization since the 1980s. Due to close
ties in social and economic aspects, single cities have expanded to form distinctive
city clusters in eastern China, such as the Beijing-
With the homogeneity-
Results show that the urbanization can induce a remarkable summer warming in YRD
city cluster region and a winter warming in BTH city cluster region. The YRD warming
in summer primarily results from the significant increasing of maximum temperature,
with an estimated urban warming rate at 0.132-
The study finds that urbanization has considerable influence on the regional climate
change. Therefore, a more reasonable urban planning should be considered in order
to mitigate regional surface warming. In addition, the climatic effect of urbanization
features obvious temporal-
###
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB428504).
Wu K, Yang X Q. Urbanization and heterogeneous surface warming in eastern China.
Chin Sci Bull, 58(12):1363-
http://csb.scichina.com:8080/kxtbe/EN/volumn/home.shtml
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11434-
Science China Press Co., Ltd. (SCP) is a scientific journal publishing company of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). For 50 years, SCP takes its mission to present to the world the best achievements by Chinese scientists on various fields of natural sciences researches.